As the world shifts towards renewable energy, solar power has emerged as a leading contender in the race to reduce carbon footprints and combat climate change. One of the key innovations that have made solar energy more accessible and financially viable for homeowners and businesses alike is solar net metering. In this blog, we’ll explore what solar net metering is, how it works, and the benefits it offers to both individuals and the broader community.
What is Solar Net Metering?
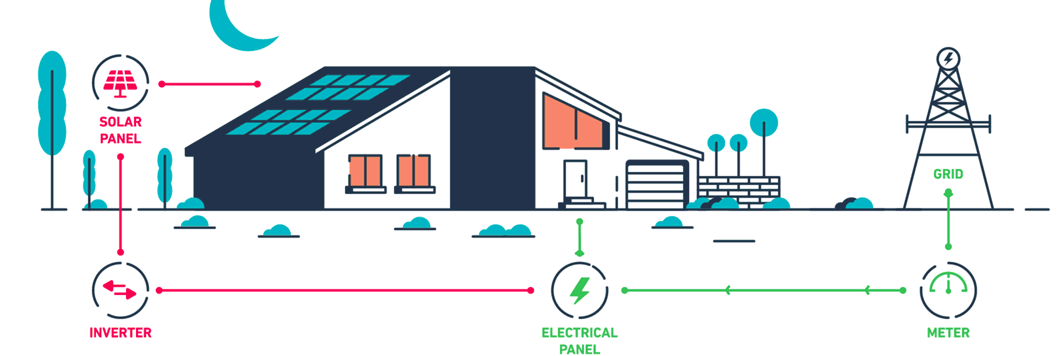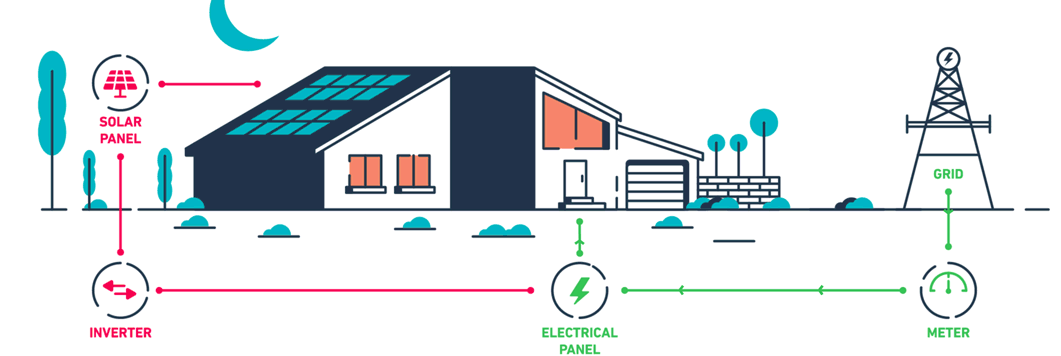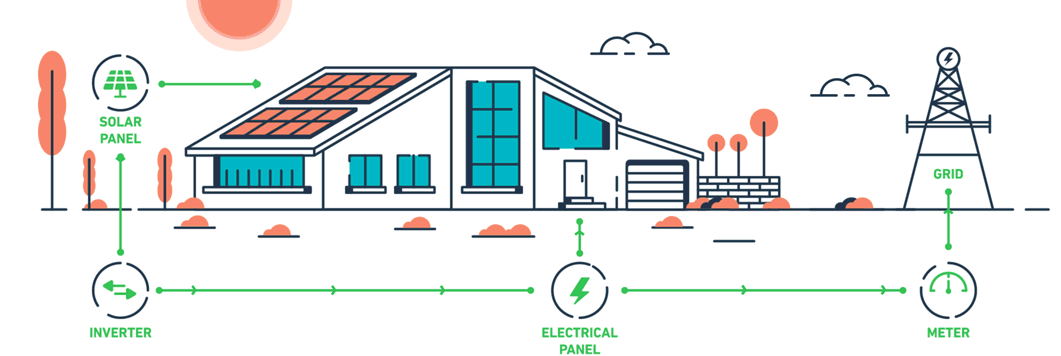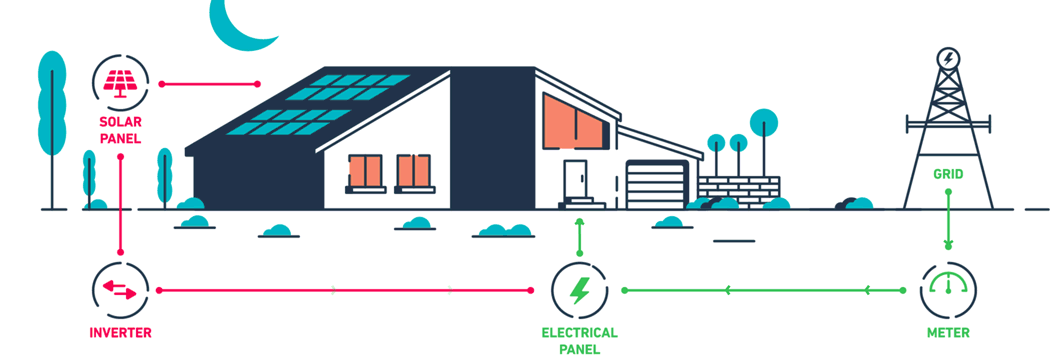
Solar net metering is a billing mechanism that allows individuals who generate their own electricity using solar panels to feed excess electricity back into the grid. Essentially, it enables a two-way relationship between the solar power system and the utility grid. When a solar panel system produces more electricity than the home or business consumes, the surplus is sent to the grid, and the owner is credited for this contribution. Conversely, when the system generates less electricity than needed, the owner draws power from the grid as usual.
How Does Solar Net Metering Work?
Installation of Solar Panels
Homeowners or businesses install solar panels on their rooftops or property, generating electricity from sunlight.
Connection to the Grid
The solar power system is connected to the local utility grid through a bi-directional meter. This meter can measure electricity flow in both directions.
Electricity Generation and Consumption
During the day, especially when the sun is at its peak, the solar panels may produce more electricity than is needed. This excess electricity is sent to the grid, and the meter runs backward, crediting the owner for the surplus.
Grid Usage
During periods when the solar panels are not producing enough electricity (e.g., at night or during cloudy days), the owner draws electricity from the grid. The meter then runs forward, recording the electricity consumption.
Billing and Credits
At the end of the billing period, the utility company calculates the net electricity used. If the owner has supplied more electricity to the grid than they have consumed, they receive a credit that can be applied to future bills.
Cost Savings
One of the most immediate benefits of solar net metering is the reduction in electricity bills. By generating their own power and receiving credits for excess production, homeowners and businesses can significantly lower their energy costs.
Energy Independence
Solar net metering promotes energy independence by allowing individuals to generate their own electricity. This reduces reliance on the grid and protects against fluctuating energy prices.
Environmental Impact
By harnessing the power of the sun, individuals reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a decrease in greenhouse gas emissions. Net metering encourages the adoption of clean energy, supporting broader environmental goals.
Grid Stability and Efficiency
Distributed generation through solar panels can enhance grid stability and efficiency. Excess solar power fed into the grid can help meet demand during peak usage times, reducing strain on the grid.
Economic Growth
The widespread adoption of solar net metering can stimulate economic growth by creating jobs in the solar installation and maintenance sectors. It also fosters technological innovation and investment in renewable energy infrastructure.
